Design Collateral
CRAFTING BESPOKE DESIGN COLLATERAL FOR VISIONARIES & ENTREPRENEURS
Well-designed marketing collateral plays a crucial role in establishing a strong and memorable brand identity for your business. It is essential for creating a cohesive and powerful brand identity that resonates with your audience, fosters trust, and sets you apart from competitors. It's an investment that has the potential to yield significant returns by driving customer engagement, loyalty, and business growth. We consider all the different touch points across your business and support the elevation of your branding with professional material you can feel proud to share.
Not sure where to begin? Get in touch today, we would love to help!

Our Design Collateral Services
-
Print advertising and digital advertising are two distinct forms of promotional strategies used by businesses and organisations to reach and engage their target audiences. While both approaches aim to convey messages and promote products or services, they utilise different media and have unique characteristics. Here's a comparison of print and digital advertising:
Print Advertising:
Medium: Print advertising involves creating promotional materials that are physically printed on tangible media, such as newspapers, magazines, brochures, posters, billboards, and direct mail.
Tangibility: Print ads are tangible and can be physically held and interacted with. This tactile experience can create a more lasting impression.
Design: Print ads use visual elements like images, colours, typography, and layout to convey messages and capture attention.
Longevity: Printed materials can have a longer lifespan compared to digital ads. Magazines, newspapers, and posters may remain visible for an extended period of time.
Targeting: Print media can be targeted based on the audience of the publication and the distribution locations.
Credibility: Established print media, such as respected newspapers and magazines, can lend credibility to the advertised content.
Local Reach: Print ads can effectively reach local audiences through community newspapers, flyers, and direct mail.
Limitations: Limited space in print materials requires concise messaging and impactful visuals. Updates or changes require reprinting.
Digital Advertising:
Medium: Digital advertising involves using digital platforms such as websites, social media, search engines, mobile apps, and email to display ads.
Interactivity: Digital ads can include interactive elements such as clickable links, forms, videos, animations, and engagement features.
Targeting: Digital advertising offers advanced targeting options, allowing ads to be shown to specific demographics, interests, behaviours, and geographical locations.
Tracking: Digital ads provide detailed analytics, allowing advertisers to track metrics like impressions, clicks, conversions, and user engagement.
Flexibility: Digital ads can be easily updated, modified, or replaced without the need for physical reprinting.
Global Reach: Digital ads can reach a global audience, breaking geographical barriers and expanding the potential customer base.
Cost Efficiency: Digital advertising often has lower costs compared to print advertising, making it more accessible for businesses of all sizes.
Real-Time Engagement: Digital ads enable real-time engagement with users through comments, likes, shares, and direct interactions.
Personalisation: Digital ads can be personalised based on user preferences and behaviours, enhancing relevance and engagement.
Businesses often use a combination of both print and digital advertising strategies to maximise their reach and impact. The choice between print and digital advertising depends on factors such as the target audience, budget, objectives, nature of the message, and the desired level of interaction and engagement.
-
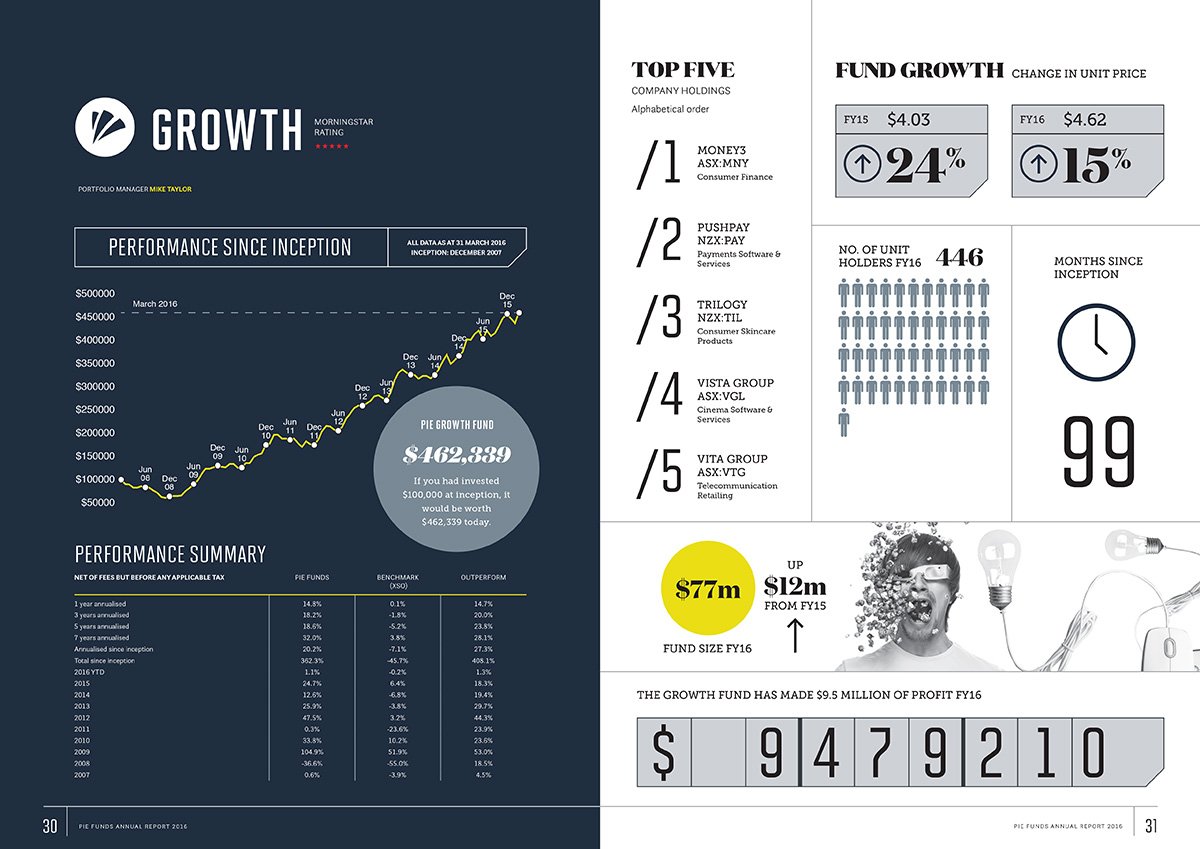
An annual report is a comprehensive document produced by a company or organisation at the end of each fiscal year. It provides shareholders, stakeholders, investors, and the general public with an overview of the organisation's financial performance, accomplishments, strategies, and other key developments over the past year. Annual reports serve as a tool for transparency, communication, and accountability, helping to inform interested parties about the organisation's activities and financial health. Here are some key components and purposes of annual reports:
Key Components of Annual Reports:
Financial Statements: These include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, which provide a detailed overview of the organisation's financial position, performance, and cash flow.
Management's Discussion and Analysis (MD&A): This section is often written by the company's management and provides an explanation and analysis of the financial results, trends, and factors that have affected the organisation's performance.
Corporate Overview: An introduction to the organisation's mission, vision, values, and key milestones achieved during the year.
Letter from the CEO or Chairman: A letter from the organisation's top leadership summarising the year's achievements, challenges, and future strategies.
Corporate Governance: Information about the organisation's leadership structure, board of directors, and governance policies.
Financial Highlights: A summary of key financial metrics, such as revenue, profit margins, earnings per share, and other relevant financial ratios.
Business Operations: Details about the organisation's core business activities, product lines, markets served, and any expansions or acquisitions.
Market Overview: A discussion of industry trends, market conditions, and competitive landscape that may have affected the organisation's performance.
Social Responsibility and Sustainability: Information about the organisation's efforts in areas such as corporate social responsibility, environmental sustainability, and community engagement.
Future Outlook: Insights into the organisation's plans, strategies, and goals for the upcoming year and beyond.
Purposes of Annual Reports:
Transparency and Accountability: Annual reports provide stakeholders, especially shareholders, with a transparent view of the organisation's financial health, strategies, and operations.
Investor Relations: Annual reports are a primary tool for communicating with current and potential investors, helping them make informed decisions about their investment.
Legal Requirement: In many jurisdictions, publicly traded companies are legally obligated to produce and distribute annual reports to shareholders.
Communication Tool: Annual reports serve as a way to communicate an organisation's accomplishments, challenges, and future plans to a wider audience, including employees, customers, partners, and the general public.
Performance Evaluation: Annual reports allow organisations to evaluate their performance against goals and benchmarks set for the year.
Historical Record: Over time, annual reports become historical records that document the organisation's evolution, growth, and achievements.
Marketing and Branding: Organisations often use annual reports as a platform to highlight their brand, values, and corporate culture.
Compliance and Regulation: In regulated industries, annual reports can help demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
Overall, annual reports provide a comprehensive overview of an organisation's financial and operational performance, and they play a vital role in building trust, credibility, and transparency among stakeholders.
-
Brochures:
Format: Brochures are typically folded pieces of paper that provide more space for content and visuals. They can have multiple folds, creating panels that unfold to reveal different sections.
Content: Brochures offer more room for detailed information. They often include sections such as company history, product features, benefits, pricing, contact details, and more.
Design: Due to their larger size and folding capabilities, brochures allow for more creative layouts and versatile design elements. They can include images, charts, graphs, and other visual aids.
Purpose: Brochures are commonly used for presenting comprehensive information about products, services, or organisations. They are suitable for trade shows, sales meetings, presentations, and other situations where in-depth information is needed.
Distribution: Brochures can be handed out directly to individuals or mailed to potential customers. They may also be displayed on brochure racks in public spaces.
Flyers:
Format: Flyers are single sheets of paper, often smaller in size compared to brochures. They can be printed on one or both sides.
Content: Flyers are more concise and focused on conveying key messages. They usually contain essential information such as event details, promotions, discounts, or a brief overview of a product or service.
Design: Flyers have limited space, so their design tends to be straightforward and to the point. They often feature bold headlines, brief descriptions, and attention-grabbing visuals.
Purpose: Flyers are suitable for quick promotions, announcements, and time-sensitive events. They're effective for distributing information in high-traffic areas or handing out to passersby.
Distribution: Flyers are often distributed in public spaces, at events, through direct mail, or as inserts in newspapers. They aim to capture attention quickly and encourage immediate action.
In summary, brochures are more comprehensive and detailed marketing materials with a focus on providing in-depth information, while flyers are concise and eye-catching pieces meant for quick promotions or announcements. The choice between using a brochure or a flyer depends on the level of information you need to convey, the target audience, the context in which the material will be distributed, and the desired impact.
-
An e-book, short for "electronic book," is a digital version of a traditional printed book that is designed to be read on electronic devices such as computers, tablets, e-readers, and smartphones. E-books offer a convenient and portable way to access written content without the need for physical books. They can encompass various genres, including fiction, non-fiction, textbooks, reference materials, self-help guides, and more. Here are some key features and characteristics of e-books:
Digital Format: E-books are primarily distributed and consumed in digital formats. They are often available in formats such as PDF, ePub, MOBI, and others, which are compatible with different types of devices and reading applications.
Portability: One of the main advantages of e-books is their portability. A single electronic device can store and provide access to numerous e-books, allowing readers to carry an entire library with them.
Readability: E-books can be customized for individual reading preferences. Readers can adjust font size, line spacing, and screen brightness to enhance readability according to their comfort.
Multimedia Integration: E-books can include multimedia elements like images, videos, and audio, enriching the reading experience and providing additional context to the content.
Search and Navigation: Digital e-books often come with search functions, hyperlinks, and navigation features that make it easy to jump to specific sections, chapters, or pages.
Interactive Features: Some e-books incorporate interactive elements such as quizzes, interactive diagrams, and links to external resources, engaging readers in a more dynamic way.
Instant Access: E-books can be purchased, downloaded, and accessed instantly from online platforms and digital bookstores, eliminating the need to wait for physical delivery.
Environmentally Friendly: Since e-books are digital, they do not require paper, ink, or physical shipping, which can contribute to reduced environmental impact compared to traditional printed books.
Distribution: Authors and publishers can distribute e-books globally without the logistical challenges of physical distribution, enabling wider reach and accessibility.
Self-Publishing: E-books have facilitated the rise of self-publishing, allowing authors to publish their works independently and reach audiences without the need for traditional publishing houses.
Sync Across Devices: Many e-reading applications and platforms offer synchronization, allowing readers to start reading on one device and continue seamlessly on another.
Cost Savings: E-books are often more affordable than printed books, as they eliminate printing, shipping, and storage costs associated with physical copies.
Annotations and Highlights: E-readers and reading applications often allow users to highlight text, add annotations, and bookmark pages, enabling active reading and note-taking.
E-books have transformed the publishing industry and reading habits, offering readers a flexible and convenient way to access literature and educational content. They have also opened new avenues for authors, educators, and content creators to share their work with a global audience.
-
EDM templates, in the context of marketing and design, stand for "Electronic Direct Mail" templates. EDMs are essentially emails that are designed and formatted for marketing purposes, such as promoting products, sharing news, providing updates, or engaging with customers. EDM templates provide a consistent and visually appealing layout for these marketing emails. Here's more information about EDM templates:
Design and Layout: EDM templates are pre-designed email layouts that include various design elements like headers, footers, columns, images, text blocks, and buttons. These templates are crafted to look visually appealing and ensure that the email's content is presented in an organized and engaging manner.
Responsive Design: A key feature of EDM templates is responsive design. Since emails are viewed on various devices, including desktops, smartphones, and tablets, responsive templates adapt to different screen sizes and resolutions, ensuring that the email's content remains readable and visually appealing across devices.
Branding: EDM templates often incorporate a company's branding elements, such as logos, color schemes, fonts, and styles. This ensures consistency with the company's overall brand identity and reinforces recognition.
Personalization: Many EDM templates offer the option to personalize emails by dynamically inserting recipient names, locations, or other relevant information. Personalized emails tend to have higher engagement rates.
Content Blocks: EDM templates typically include various content blocks that can be customized with text, images, videos, and other multimedia elements. These blocks make it easy to create visually appealing emails without the need for extensive coding.
Call-to-Action (CTA): Effective EDM templates often include strategically placed CTAs, such as buttons or links, to encourage recipients to take specific actions, like making a purchase, signing up for an event, or visiting a website.
Drag-and-Drop Editors: Many email marketing platforms provide drag-and-drop editors that allow marketers to easily customize EDM templates without needing advanced design or coding skills. This user-friendly approach streamlines the process of creating and sending marketing emails.
A/B Testing: Some EDM platforms allow you to test different versions of your email by creating variants of the template. This helps marketers determine which design or content elements are more effective in achieving their goals.
Analytics and Tracking: After sending EDMs, platforms often provide analytics that allow marketers to track metrics such as open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates. This data helps gauge the effectiveness of the template and the email campaign as a whole.
EDM templates are a valuable tool for businesses and marketers looking to create engaging and consistent email marketing campaigns. By using well-designed templates, marketers can save time, maintain brand consistency, and enhance the overall impact of their email communications.
-
An information pack is a collection of materials and documents that are assembled and distributed to provide comprehensive information on a specific topic, event, product, service, or organisation. Information packs are often used for educational, promotional, or informative purposes, and they can be physical or digital in nature. Here's more about information packs:
What are Information Packs used for?:
Marketing and Promotion: Information packs are often used to promote products, services, or events. They provide potential customers with detailed information about what's being offered.
Educational Purposes: Information packs can serve as educational resources in schools, universities, workshops, and seminars.
Business Proposals: Companies may create information packs as part of business proposals to provide potential clients with a comprehensive understanding of their offerings.
Orientation and Training: Organisations may use information packs to onboard new employees, providing them with information about company policies, procedures, and culture.
Events and Conferences: Information packs can provide attendees with schedules, speaker profiles, and other relevant event details.
Information packs are designed to convey information clearly and effectively. They play a crucial role in communicating complex information, promoting understanding, and facilitating informed decision-making. The content and format of an information pack depend on the target audience, purpose, and the depth of information being conveyed.
-
Magazine design refers to the process of creating visually appealing and engaging layouts for magazines. It involves the arrangement of text, images, graphics, and other elements in a cohesive and attractive manner to communicate information, tell stories, and convey the overall theme or focus of the magazine. Magazine design is a critical aspect of print media, as it plays a significant role in capturing readers' attention, guiding their reading experience, and reflecting the magazine's brand identity. Here are some key elements and considerations in magazine design:
Layout and Composition: Designers arrange content on each page using a combination of columns, grids, and whitespace. The layout determines the flow of information and ensures a balanced distribution of elements.
Typography: The choice of fonts, sizes, styles, and spacing affects the readability and visual impact of the magazine. Headlines, subheadings, body text, and captions all require thoughtful typographic choices.
Images and Graphics: High-quality images, illustrations, infographics, and other visual elements contribute to the magazine's visual appeal. These visuals help convey messages and break up text-heavy pages.
Colour Scheme: A consistent color palette enhances the magazine's visual identity and reinforces branding. Colour choices influence the mood and tone of the content.
Cover Design: The cover is a critical component that needs to grab readers' attention and communicate the magazine's content or theme. Eye-catching visuals, compelling headlines, and a clear layout are essential.
Headlines and Subheadings: Effective headlines summarise the main content and attract readers' interest. Subheadings help break down longer articles and guide readers through the content.
Grids and Columns: Grid systems ensure a structured layout and help maintain consistency across pages. Columns provide a framework for organising content and maintaining readability.
Whitespace: Whitespace (also known as negative space) gives the design room to breathe and prevents visual clutter. It also highlights important elements and improves readability.
Hierarchy: Designers use visual cues like font sizes, colours, and placement to establish a clear hierarchy of information, guiding readers through the content in a logical order.
Pull Quotes and Callouts: Pull quotes and callout boxes draw attention to key quotes, insights, or important details, adding visual interest and breaking up text.
Continuity and Consistency: A consistent design approach throughout the magazine ensures a cohesive reading experience. Elements such as headers, footers, page numbers, and typography should remain uniform.
Variety and Rhythm: Designers create visual interest by varying page layouts, alternating between text-heavy and image-focused pages, and introducing different design elements.
Margins and Bleeds: Proper margins and bleeds are essential for accurate printing. Bleed refers to elements that extend beyond the edge of the page to ensure there are no white borders after trimming.
Magazine design requires a combination of artistic creativity and attention to detail, as well as an understanding of the target audience and the magazine's content. The goal is to create a visually engaging experience that captivates readers, facilitates content consumption, and reflects the magazine's brand identity and editorial direction.
-
A PowerPoint presentation is a visual and multimedia communication tool created using Microsoft PowerPoint software. It is commonly used to deliver information, convey ideas, and present data in a structured and engaging manner. PowerPoint presentations consist of slides, each of which can contain various types of content, such as text, images, charts, graphs, videos, animations, and more. These slides are displayed sequentially, often accompanied by a presenter's narration or commentary. Here are some key features and components of a PowerPoint presentation:
Slides: The fundamental building blocks of a PowerPoint presentation are slides. Each slide represents a single "page" of content that can be filled with various types of multimedia elements.
Title Slide: The title slide is typically the first slide in a presentation and contains the presentation's title, the presenter's name, the date, and potentially the company or organization's logo.
Content Slides: These slides make up the bulk of the presentation. They can contain text, images, charts, diagrams, bullet points, and other content to support the presenter's message.
Text: Presenters can add textual content to slides using various fonts, sizes, and styles. Bullet points, paragraphs, and headings are commonly used to structure the information.
Images: Presenters can insert images and graphics to illustrate concepts, provide visual context, or enhance the visual appeal of the slides.
Charts and Graphs: PowerPoint offers tools to create various types of charts and graphs to display data and trends in a visually appealing way.
Videos and Audio: Multimedia elements like videos and audio clips can be embedded into slides to enhance engagement and provide additional context.
Animations and Transitions: Animations allow elements on a slide to appear, move, or transition in a dynamic manner. Slide transitions control how one slide transitions to the next.
Presenter Notes: Presenters can include speaker notes that are not visible to the audience but are helpful for guiding the presentation and providing additional information.
Slide Master: PowerPoint provides a slide master feature that allows users to create a consistent design template for all slides, ensuring a unified look and feel.
Templates: PowerPoint offers pre-designed templates that provide ready-to-use designs and layouts for various presentation purposes.
Slide Sorter: The slide sorter view allows users to easily rearrange, duplicate, or delete slides in the presentation.
Presenter View: When presenting, the presenter can use the "Presenter View" to see notes, upcoming slides, and a timer while the audience sees only the current slide.
PowerPoint presentations are commonly used in business meetings, educational settings, conferences, and various other contexts where information needs to be conveyed visually and effectively. However, it's important to design presentations thoughtfully, ensuring that the content is clear, engaging, and aligned with the goals of the presentation.
-
Social media templates are pre-designed layouts that provide a framework for creating consistent and visually appealing content for various social media platforms. These templates come in various formats, such as images, graphics, videos, and animations, and are designed to help individuals and businesses maintain a cohesive and recognisable brand presence on social media. Social media templates streamline the content creation process and ensure that posts, stories, and other updates have a professional and polished look. Here's more about social media templates:
Key Elements of Social Media Templates:
Design Elements: Social media templates incorporate design elements like color schemes, fonts, logos, and other brand elements that align with your brand identity.
Layout: Templates define the arrangement of text, images, graphics, and other visual elements on a post. This layout consistency maintains a unified look across your social media profiles.
Sizes: Social media platforms have specific dimensions for different types of content (e.g., profile pictures, cover photos, posts, stories). Templates are created in the appropriate sizes for each platform to ensure optimal display.
Content Types: Templates cover various types of content, including regular posts, promotional graphics, stories, cover images, and more.
Editable Fields: Templates often include editable fields where you can add your own text, images, and other content. This allows you to customise the template to suit your specific message or promotion.
Visual Elements: Social media templates may include placeholders for images, icons, illustrations, and other visual elements that are relevant to your brand and content.
Call-to-Action (CTA): Templates might include buttons or text fields for adding CTAs to encourage users to take specific actions, like visiting a website, signing up, or purchasing a product.
Advantages of Using Social Media Templates:
Consistency: Templates ensure that your social media content maintains a consistent visual style and branding, reinforcing recognition and professionalism.
Time-Saving: Templates streamline the content creation process, reducing the time spent on designing each post from scratch.
Professionalism: Well-designed templates enhance the overall quality of your social media content, giving it a polished and professional appearance.
Brand Identity: Templates reinforce your brand identity by consistently using the same colours, fonts, logos, and design elements across your social media profiles.
Efficiency: Templates can be reused and adapted for different posts, campaigns, and announcements, saving you the effort of designing new content for every update.
Engagement: Visually appealing and well-structured content is more likely to capture users' attention and encourage engagement.
Accessibility: Templates ensure that your content is optimised for various devices and screen sizes, making it accessible to a wider audience.
Social media templates are available through various design tools and software, as well as online platforms that offer customisable templates for different social media platforms. They cater to a range of needs, from individual influencers to businesses looking to maintain a strong and consistent online presence.
-
Stationery design refers to the creation of a set of coordinated and branded paper-based materials that represent a company or individual's visual identity. These materials are typically used for various business communications and interactions. Stationery design goes beyond just letterhead and envelopes; it encompasses a range of items that contribute to a cohesive and professional brand image. Some common components of stationery design include:
Letterhead: This is a printed sheet of paper that includes the company's logo, name, address, contact information, and sometimes a watermark or background design. It is typically used for formal correspondence, such as business letters, invoices, and official documents.
Envelopes: Envelopes are designed to match the letterhead and often include the company logo and return address. They provide a consistent and polished appearance when mailing important documents.
Business Cards: Business cards are small, portable pieces of stationery that contain the individual's or company's contact information, logo, and often a tagline. They are exchanged during networking events, meetings, and other professional interactions.
Note Cards: Note cards are smaller than letterhead and are used for shorter correspondence, thank-you notes, or personal messages. They may have the company logo or monogram on them.
Folders: Presentation folders are used to hold documents, brochures, and other materials. They often have a slot for business cards and can be customised with the company's branding.
Notebooks and Notepads: Customised notebooks and notepads with the company logo and branding can be used internally for employees or given as promotional items to clients.
Stamps and Seals: Custom stamps and seals with the company's logo or address can be used to add a branded touch to envelopes and other materials.
Labels and Stickers: Branded labels and stickers can be used for packaging, promotional materials, and other items.
Digital Templates: In the digital age, stationery design also extends to digital templates for emails, presentations, and other digital communications. These templates maintain the brand identity in electronic communications.
The purpose of stationery design is to create a consistent and professional visual identity across all printed materials used by a company. This consistency enhances brand recognition, establishes credibility, and reinforces the overall brand image in the minds of clients, partners, and stakeholders. Effective stationery design should reflect the company's values, tone, and style while maintaining a cohesive and visually appealing appearance.
Will you be our next design collateral project?
From Annual Reports, Magazines, Catalogues, Presentations and Book Covers we can take it from concept right through to finished product.
Attract the right audience to your business today. I can’t wait to hear about your project and vision. Let’s talk!